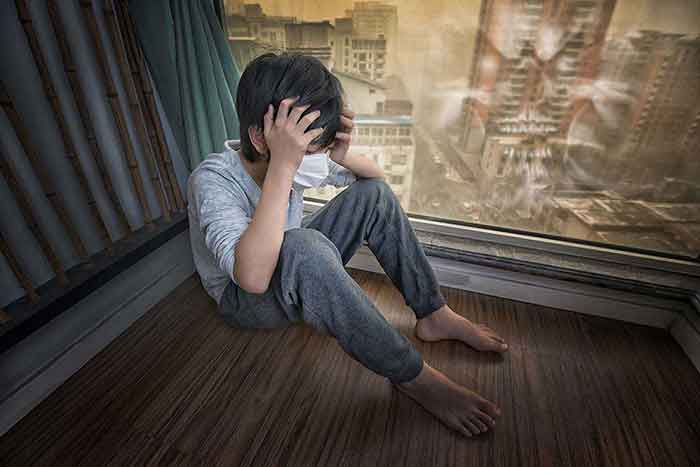
Indoor Air Pollution is a Problem for our Health
Most of us are aware of the problems we face with outdoor air pollution and the effects that pollution has on our health and the environment.
Air pollution outdoors comes from many different sources, some of which include: vehicle emissions, fuel and oils, natural gas, manufacturing, power plants, chemical production, agriculture, dust and pollen.
Although outdoor air pollution is mainstream news, little is understood or reported about the pollution inside our homes.
Considering we spend 80% of our time indoors, whether, at home or work, we are sitting in sometimes heavily polluted environments that are causing our health and well-being to suffer.
What Causes Indoor Air Pollution?
Indoor air pollution comes from volatile organic compounds, formaldehyde, particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide. As well as biological pollutants such as dust, house dust mites, mould and mildew, and pet dander.
Chemical vapours such as volatile organic compounds and formaldehyde emit from many products and materials used in the home and our places of work. Such as cleaning materials, air fresheners, diffusers, paint, varnishes, wallcoverings, synthetic carpets, synthetic upholstery, newly installed flooring, MDF furniture, particleboard, fuel-burning stoves, fireplaces, heating and cooling systems.
THE HEALTH COSTS OF TOXIC AIR ARE ESTIMATED AT £20 BILLION A YEAR (ROYAL COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & ROYAL COLLEGE OF PAEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH)
Biological Pollutants Contributing to Poor Indoor Air Quality
Biological pollutants come from living organisms within our environment. They include animal dander, cat saliva, house dust mites, pollen from trees and plants, bacteria and viruses.
People only suffer allergic reactions after repeated exposure to a pollutant. However, that reaction can occur immediately upon re-exposure or after multiple exposures.
As a result, people who have noticed only mild allergic reactions, or no reactions at all, may suddenly find themselves very sensitive to particular allergens.
Children, seniors, and people with breathing problems or allergies are particularly susceptible to airborne biological pollutants.
Mould, dust mites, pet dander and pest droppings can trigger asthma. Also, moulds and pollens can cause allergic reactions in a significant portion of the population.
Carbon Monoxide Contributing to Poor Indoor Air Quality
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odourless and colourless gas. The effects of CO exposure can vary significantly from person to person depending on age, overall health and the concentration and length of exposure. Because it is impossible to see, taste or smell, Carbon monoxide poisoning can make you sick before you’re even aware of a leak.
CO poisoning varies from mild dizziness to loss of consciousness, and symptoms will worsen with continued exposure. If there is a lot of carbon monoxide in the air, poisoning can happen within hours.
Gas cookers, wood-burning stoves and heaters produce large amounts of carbon monoxide, which can be lethal. They also emit other harmful gases such as carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, and sulphur dioxide. Carbon monoxide from car exhaust fumes can seep through internal doors in garages and release poisonous vapours into the home.
Volatile Organic Compounds Contributing to Poor Indoor Air Quality
Volatile organic compounds, or VOCs, are organic chemicals that vaporise at room temperature. VOCs are emitted as gases from burning wood and coal and released from many household goods such as paint, cleaning products, carpets and furniture.
Also, high temperature and humidity levels increase concentrations of some toxins. Without proper ventilation, these toxins build up within the home, posing a threat to health.
VOC Levels are Two to Five Times Higher Indoors
A study by the Environmental Protection Agency found levels of about a dozen common VOCs to be two to five times higher inside homes than outside, regardless of whether the houses were in rural or highly industrial areas. And concentrations of many VOCs are up to ten times higher indoors than outdoors.
The most common VOCs found in the home are formaldehyde, acetone, ammonia, methyl alcohol, ethyl acetate, toluene, xylene and benzene. And in 2004, the International Agency for the Research on Cancer classified formaldehyde as a carcinogen.
Exposure to VOCs can cause various adverse health effects such as a runny nose, burning sensations in the eyes, sore throat and headaches; long-term exposure can cause allergies and asthma.
Some immediate effects of VOC exposure are similar to colds or other viral diseases, which makes it hard to identify the cause of the problem.
The VOC levels emitted into the air depend on temperature, humidity, seasonal weather and ventilation. Toxic emissions will increase with higher temperatures and decrease with lower temperatures.
Common Volatile Organic Compounds Found in the Home
The most common volatile organic compounds found in the home are Acetone, Ammonia, Benzene, Ethyl Alcohol, Methyl Alcohol, Alcohol, Ethyl Acetate, Formaldehyde, Toluene, Xylene, Chloroform and Butanal.
AIR QUALITY IS THE SINGLE BIGGEST ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARD IN THE WORLD (WHO)
The Health Effects of Exposure to Indoor Air Pollution
The EPA says health effects may appear shortly after a single exposure or repeated exposure to a pollutant.
Some health effects associated with air pollution are: irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, headaches, dizziness, and fatigue; immediate effects are usually short-term and treatable.
Some effects are similar to those from colds or other viral diseases, so it is often difficult to determine if the symptoms result from indoor air pollution.
As a result, paying attention to when and where symptoms occur is essential. For example, suppose symptoms decrease when away from the area. In that case, it may be wise to identify potential causes within the home or workplace.
The indoor conditions may worsen some health effects, where there is insufficient clean air entering the building or the temperature, humidity, and heating are not evenly distributed.
Your Home’s Health Affects your Health and Wellbeing
Regardless if you are experiencing health problems, it is advisable to keep your home clean using non-toxic cleaners, ventilate regularly and purchase non-toxic alternative products and furnishings.
Poor health due to indoor air pollution can affect you years after repeated exposure, causing health issues such as respiratory ailments, heart disease, and cancer.
Despite many harmful effects caused by pollutants commonly found in indoor air, it is unclear what concentrations or periods of exposure are required to cause specific health problems. People also react very differently to exposure to indoor air pollutants.
Continuing research is needed to understand better which health effects occur following regular exposure to average pollutant concentrations in homes and which appear following exposure to higher concentrations of pollutants for short periods.
Top Tips to Improve Indoor Air Quality
Modern homes that are tightly sealed cant breathe, trapping inside them a toxic soup of pollutants – open windows and doors throughout the day to replenish the air.
Increase ventilation when cooking by opening windows and always using an extractor fan. Make sure you replace filters regularly because old filters will no longer be doing the job of catching harmful pollutants.
Sometimes, we don’t have sufficient ventilation in our homes or places of work; in this case, we invest in an air purifier to help remove pollutants from the air. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when removing filters. And clean the air purifier regularly.
Buy pre-loved furniture from auction sites like eBay, Gumtree and Pre-loved because the furniture will have already gone through the off-gassing process, where VOCs emit into the environment polluting the air.
Always use non-toxic paint. Look out for low or minimal VOC content; you will find this information on the side of the paint tin.
Use non-toxic cleaning products, and always check the label; the packaging may present as eco-friendly; however, this is sometimes greenwashing, where a company lures you into believing it is something it isn’t.
Never use air fresheners or diffusers that aren’t made from natural ingredients; these are highly toxic and one of the worst offenders for air pollution.
Instead of buying synthetic carpets made from polypropylene that emit VOCs and cause indoor air pollution, choose a natural alternative such as wool, sisal, jute or seagrass.
Opt for natural alternatives for your soft furnishings, such as organic cotton, linen and hemp, because most fabrics are synthetic or have a high percentage of synthetic materials which emit pollution into your home, adding to air pollution.
References
EPA. Introduction to Indoor Air Quality. Available from: https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/introduction-indoor-air-quality
Asthma + Lung UK. Indoor Air Quality. Available from: https://www.blf.org.uk/support-for-you/indoor-air-pollution/causes-and-effects
British Coatings Federation Ltd. VOCs and Air Quality. https://coatings.org.uk/page/VOCsAndAirQuality