Volatile Organic Compounds, What are they and Where are they Found
Volatile organic compounds have high vapour pressure and low water solubility. Many VOCs are chemical products made and used by humans, such as paints, pharmaceuticals, and refrigerants.
Typically, Volatile Organic Compounds are industrial solvents such as trichloroethylene, oxygenates from fuels such as methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), or by-products of water treatment such as chloroform. Petrol fuels, hydraulic fluids, paint thinners, and dry-cleaning agents are all examples of VOCs.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted as gases from certain solids or liquids. VOCs are emitted from many products and goods that are used within the home or at work. Examples include building materials, furnishings, MDF and particleboard, furniture, paint, varnishes, glues, paint strippers, cleaning goods, synthetic materials and flooring, and office equipment such as copiers and printers. This is a partial list; the products go into the thousands.
The concentration of VOCs indoors is up to ten times higher than outdoors. Exposure to VOCs can have both short-term and long-term health implications, and VOCs release while you use them and emit while stored if not done correctly.
Furthermore, the VOC levels emitted into the air depend on temperature, humidity, seasonal weather and ventilation. Toxic emissions will increase with higher temperatures and decrease with lower temperatures. Without adequate ventilation, the toxins will build up inside the home, posing a health risk.
A study by EPA’s Total Exposure Assessment Methodology (TEAM) found levels of about a dozen common VOCs to be two to five times higher inside homes than outside, regardless of whether the houses were in rural or highly industrial areas. And concentrations of many VOCs are up to ten times higher indoors than outdoors.
The most common VOCs found in the home are formaldehyde, acetone, ammonia, methyl alcohol, ethyl acetate, toluene, xylene and benzene. In 2004, the International Agency for the Research on Cancer classified formaldehyde as a carcinogen.
Volatile Organic Compounds Health Effects of Exposure
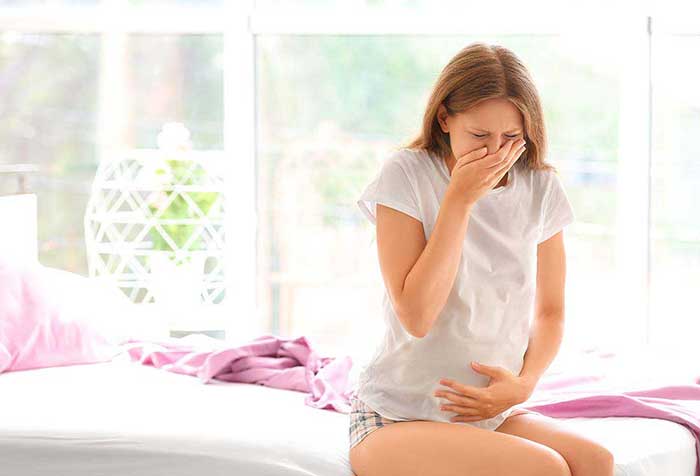
Various health effects can result from exposure to VOCs, such as a runny nose, burning sensations in the eyes, sore throat and headaches; long-term exposure can damage the liver, kidneys and central nervous system and trigger allergies and asthma. Furthermore, some VOCs cause cancer in animals and others are suspected or known to cause cancer in humans.
Because VOCs can cause symptoms similar to a cold or viral infection, it is often difficult for people to tell the difference between an illness and an immediate consequence of exposure. You are likely experiencing a reaction to volatile organic compounds if your symptoms lessen or disappear when you leave home.
The risk to your health while living in a home polluted with many different chemicals will depend significantly from person to person and, of course, the type and combination of chemicals that are emitted and over what period.
An example is bringing a new item of furniture into the home; if it’s made from a composite wood like MDF or has been chemically treated, the furniture needs to go through a period to off-gas the chemicals. Furniture is particularly toxic when brand new; the toxicity levels lessen over time.
In addition another example is painting a room in your home. If you’re not using a low VOC paint, during the paint application, VOCs will off-gas into the room and continue for some time. Also, temperature changes will continually cause the paint to off-gas harmful VOCs over time.
Some people will be more susceptible to illness brought on by VOC exposure, those with respiratory issues such as asthma as well as young children, the elderly and those who suffer from chemical sensitivities.
Volatile Organic Compounds Health Effects from Exposure
- Irritation of the eyes, nose and throat
- Burning of the eyes, nose and throat
- Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and chest pain
- Breathing problems
- Skin irritation
- Allergies and asthma
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Lethargy
- Fatigue and drowsiness
- Confusion
- Poor concentration
- Mental fatigue
- Irritability
Common Volatile Organic Compounds Found in the Home
Acetone, Ammonia, Benzene, Ethyl Alcohol, Methyl Alcohol, Alcohol, Ethyl Acetate, Formaldehyde, Toluene, Xylene, Chloroform and Butanal are the most common volatile organic compounds found in homes.
Furnishings
- Particleboard, chipboard, plywood, pressed wood, and MDF
- Wallpaper and wallcoverings
- Carpet: synthetic carpet, underlay, laminate flooring
- Upholstered furniture: synthetic fibres and polyurethane foam
- Textiles: synthetic fibres
Cleaning & Homewares
- Cleaning products, washing up liquid, polishes, window cleaners, stain removers, fabric, and leather cleaners
- Air fresheners, reed diffusers and scented candles
- Refuse sacks and grocery bags
- Dry-cleaned clothes
Decorating
- Furniture stains, varnishes, wax and resins
- Varnish remover and paint remover
- Adhesive
- Paint
Personal Care Products
- Perfume and deodorant
- Shampoo, body wash, hand sanitiser and hairspray
- Toothpaste and mouthwash
- Nail varnish and nail varnish remover
List of Chemicals Found in Household Goods
Acetone
- Particle board – Furniture and building materials
- Paint remover
- Furniture wax
- Furniture stains
- Cleaning products
Ammonia
- Synthetic fibres used to make textiles
- Paper
- Window cleaners
- Floor waxes
- Cleaning products
Benzene
- Furniture stains and varnishes
- Varnish removers
- Adhesives
- Paints
- Furniture wax
- Detergents
- Floor coverings
- Particleboard
- Wall coverings
Ethyl Alcohol
- Cleaning detergents
- Washing up liquid
- Polishes
- Perfume
- Deodorant
- Shampoos
- Body wash
- Toothpaste
- Mouth wash
- Hand sanitiser
Methyl Alcohol
- Nail varnish
- Nail varnish remover
- Perfume
- Rubbing alcohol
- Hair spray
Alcohols
- Carpeting
- Floor covering
- Paint
- Particleboard
- Wallcovering
- Furniture stains and varnishes
- Adhesives
- Cosmetics
Ethyl Acetate
- Nail varnish
- Nail varnish remover
- Perfume
- Hair spray
Formaldehyde
- Floor coverings
- Fabrics
- Refuse sacks
- Chipboard
- Plywood
- Upholstered furniture
- Carpets
- Plywood
- Pressed wood products
- Adhesives
- Caulking compounds
- Ceiling tiles
- Draperies
- Fabrics
- Floor coverings
- Gas stoves
- Grocery bags
- Paints
- Particleboard
- Permanent press clothing
- Stains & Varnishes
- Upholstery
Toluene
- Cement (PVC, contact, model)
- Adhesives
- Bio effluents- emanate from the bodies of humans or animals
- Caulking compounds
- Ceiling tiles
- Computer VDU screens
- Electrophotographic printers
- Floor coverings
- Paints
- Particleboard
- Photocopiers
- Stains and varnish
- Wallcoverings
Xylene
- Degreasers
- Bio effluents
- Ceiling tiles
- Computer VDU screens
- Electrophotographic printers
- Floor coverings
- Paints
- Particleboard
- Photocopiers
- Stains & Varnish
- Wallcoverings
Chloroform
- Chlorinated tap water
Butanal
- Candles
- Gas stoves
- Barbecues
- Furnishings:
- Synthetic carpets
- Floor tiles
- Laminates
- Furniture
- Soft furnishings
- Curtains
- Plastics
- Polyurethane foam
- Carpet underlay, carpet adhesive
- Particleboard, plywood, cabinetry
Top 5 Tips to Eliminate Volatile Organic Compounds

1. Keep your home well ventilated during and after painting, as some paints release VOCs and are highly toxic. In addition, tightly sealed buildings have little ventilation which traps toxic fumes inside.

2. Increase ventilation when using toxic cleaning materials such as bleach; they contain many harmful pollutants, such as VOCs and formaldehyde.

3. Replace toxic cleaning materials with products that are environmentally friendly. Also, avoid aerosols and sprays as this harm the ozone layer.

4. Do not use air fresheners they release harmful toxins and VOCs into the atmosphere. As an alternative use essential oils, they are natural and also have many healing benefits.

5. Avoid synthetic carpets as they emit formaldehyde and VOCs. All contributing to indoor air pollution.
References
MDH. Volatile Organic Compounds in your Home. Available from:
https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/air/toxins/voc.htm
EPA. Volatile Organic Compounds Impact Indoor Air Quality. Available from: